Bladder cancer
. Bladder cancer is the seventh most common cancer diagnosis in worldwide, with 500 000 new cases and 200 000 deaths in 2018 (Globocan 2018).
. More than 2.7 million people have a history of bladder cancer worldwide.
. At the initial diagnosis of bladder cancer, more than 80% of cases are diagnosed as non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
. Due to the very high recurrence rate (>80%), NMIBC patients require lifelong surveillance with periodic follow-up cystoscopy (an unpleasant invasive exam) and urine cytology (utility limited because cytology has a low sensitivity in detecting low-grade tumors).
. The bladder cancer is the most expensive cancer.
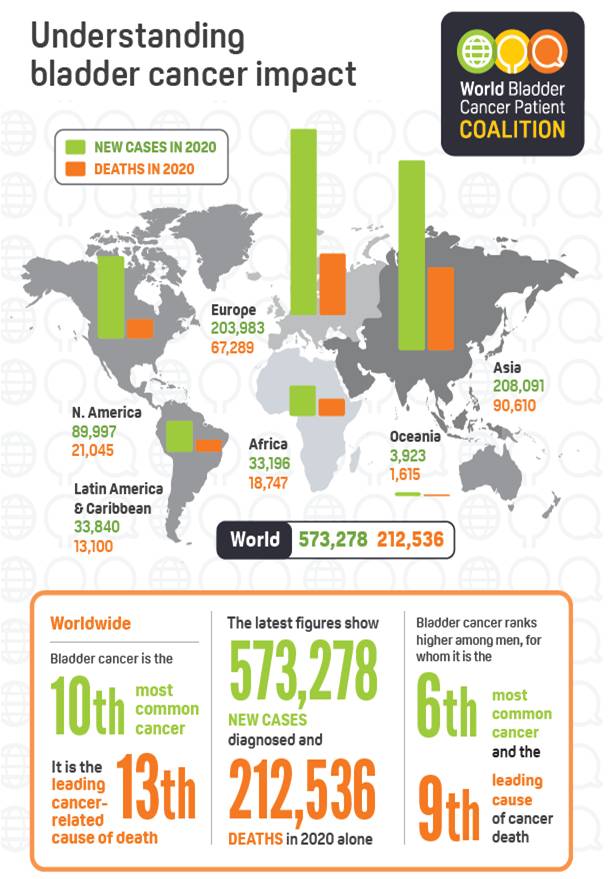
Bladder cancer incidence and mortality statistics worldwide in 2020
Risk factors

Tobacco smoking
. Cigarette smoking most important
factor related to bladder cancer
. More than 50% due to cigarette
smoking
. Confers a twofold increased of
bladder cancer than nonsmokers; dose-related
. Cigarette smoking most important factor related to bladder cancer
. More than 50% due to cigarette smoking
. Confers a twofold increased of bladder cancer than nonsmokers; dose-related

Occupational and environmental exposure
. Carcinogenic chemical substances (e.g., aromatic amines, paints and solvents) represent up to 25% of bladder cancer
. Workers in chemical, petrochemical, plastic, paint and rubber industry
Diagnostic: How is bladder cancer diagnosed?
 Symptoms
Symptoms
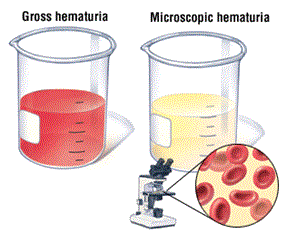
. Gross heamturia: Visible blood in the urine
. Miscroscopic hematuria: Presence of microscopic red cells in the urine
. Urinary discomfort
. Frequent urination
. Bladder spasms
. Gross heamturia: Visible blood in the urine
. Miscroscopic hematuria: Presence of microscopic red cells in the urine
. Urinary discomfort
. Frequent urination
. Bladder spasms
 Urine cytology
Urine cytology
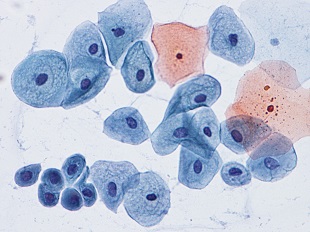
. Laboratory test in wich a sample urine is checked under microscope for abnormal cells
. Cytologist dependent
. Medium sensitivity for high-risk bladder cancer (40-50%)
. Low sensitivity for low-risk bladder cancer (20-40%)
. Low sensitivity for detection of recurrences (38-65%)
 Bladder cystoscopy
Bladder cystoscopy
 Bladder cystoscopy
Bladder cystoscopy
. Cystoscopy is the gold standard procedure for diagnosis and surveillance of bladder cancer
. Invasive exam, uncomfortable and costly
. Urologist dependent
. High accurate with sensitivity and NPV >95%
. Risks and side effects: swelling of the urethra, blood in urine, pain to urinate, microbial infection
 Histology analysis
Histology analysis
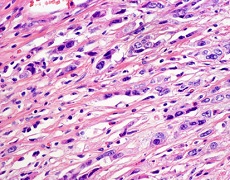
. Histological analysis performed by the pathologist
. Examination of tissue samples and surgical specimens under a microscope
. Determination whether the tumor is benign or malignant, as well as the malignancy potential
. Bladder cancer classification based on the type, grade and stage



